The process of indexing is crucial in the realm of search engine optimization (SEO), since it affects whether a web page will be included in a search engine’s database (index) and therefore appear in search results. A website must undergo indexing in order for users to see it on search engines like Google. The notion of indexing in SEO will be thoroughly covered, along with an explanation of how it functions in relation to Google. We will investigate the goal of indexing, the variables that affect it, the procedure involved, and recommended practices to guarantee efficient indexing of web pages.
What is Indexing in SEO?
Indexing in the context of SEO, indexing refers to the process through which search engines such as Google collect, analyze, and store information from web sites in order to include it in their massive databases known as the search index. This index acts as a data repository for the search engine, allowing it to give relevant and timely results to user searches.
When a website or web page is indexed, it becomes discoverable by search engine bots and accessible to users via search engine results pages (SERPs). Indexing is an important step because even if a website is well-optimized, it will not appear in search results if it is not indexed. Indexing comprises several processes, from crawling through rendering and eventually adding pages to the index.
The Evolution of marketing new blog https://digitalsparrow.co/the-evolution-of-marketing-embracing-the-digital-frontier/
Importance of Indexing for Websites.
Indexing is essential for websites to be found and ranked in search engine results. Here are some key reasons why indexing is crucial for SEO:
Visibility: When a page is indexed, it has the potential to appear in search results for related searches. The more pages that are indexed, the more likely it is that you will receive organic traffic from search engines.
Ranking: Indexed pages can be ranked depending on their relevance and authority. The more optimized a page is for specific keywords, the higher it will rank in search results.
Website Updates: Indexing ensures that search engines are aware of current modifications or updates to a website’s content. Without effective indexing, new information or modifications will not be reflected in search results.
Crawl Budget Efficiency: Search engines provide a limited crawl budget to each website, which governs how frequently they crawl and index pages. Proper indexing allows search engines to focus on useful and relevant content during their crawl.
How Google Indexes Web Pages
Google, being the most popular search engine, has a complex process for indexing web pages. Understanding this process is essential for optimizing websites for effective indexing. The indexing process in Google involves the following main steps:
Googlebot and Crawling: Googlebot is Google’s web-crawling bot, responsible for discovering and retrieving web pages from the internet. It begins by browsing a list of URLs built by previous crawls and sitemaps provided by website owners. As it crawls the web, it accumulates HTML content, which includes text, photos, and other resources. Googlebot follows links on each page, discovering new URLs to crawl and adding them to the crawl queue.
Rendering and Indexing: When Googlebot retrieves a web page, it goes through the rendering process, in which it reads the website’s HTML, executes JavaScript, and renders the page like a conventional web browser would. This phase is critical since some content may only be visible or accessible after JavaScript execution, and if Googlebot does not render it, the content may not be indexed.
After rendering, Googlebot analyses the content, including text, photos, and other resources, to determine the page’s context and relevance to certain keywords. It then extracts and indexes this information, allowing the page to appear in search results for relevant queries.
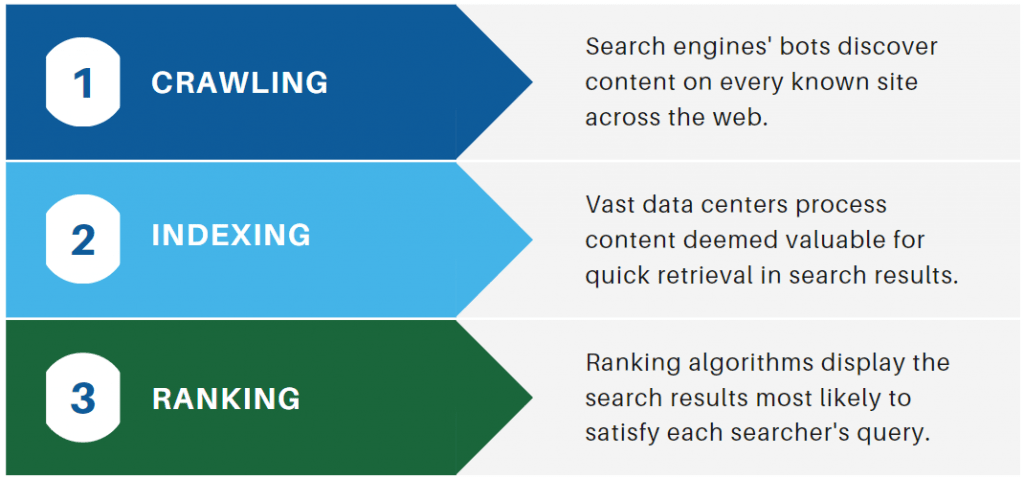
Indexing Queue and Prioritization: Google uses an indexing queue to regulate the order in which pages are indexed. Not all pages are indexed immediately; some may take some time to be analyzed and added to the index. Google priorities indexing depending on a variety of characteristics such as page authority, freshness, and user popularity. Pages with high authority from credible websites and pages with frequent updates are typically indexed more frequently.
It is crucial to realize that indexing does not guarantee immediate ranking in search results. Ranking is determined by various criteria, including relevancy, competition, and the quality of the page’s content.
Factors Influencing Indexing
Several factors influence how search engines, including Google, index web pages. Optimizing these factors can improve the chances of successful indexing and visibility in search results. Here are some critical factors.
Website Architecture and Structure: A well-organized website with a clear hierarchy and logical linking structure is easier for search engines to crawl and index. Internal linking is used by properly built websites to direct search engine bots to important pages and disperse link equity throughout the site.
Sitemap and Robots.txt: An XML sitemap is a file that provides search engines with a list of all the important pages on a website. Submitting the sitemap to Google via Google Search Console aids in faster and more effective crawling. The robots.txt file, on the other hand, can be used to tell search engines on certain pages or directories to prohibit crawling and indexing.
Page Quality and Content: High-quality, relevant, and distinctive material is more likely to get indexed and rated. Because Google strives to provide the best possible results to visitors, pages with thin or duplicate content may not be indexed or ranked as well. Concentrate on producing useful content that meets the needs of users.
Mobile-Friendly Design: Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, which means that it ranks and indexes pages based on their mobile versions. Make sure your website is mobile-friendly and offers a consistent user experience across all devices.
Page Speed and Performance: Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing, which means that it ranks and indexes pages based on their mobile versions. Page speed is an important consideration for both user experience and SEO. Pages that load faster are more likely to be crawled and indexed quickly. Optimizing page speed and performance is critical to ensuring search engines can crawl and index your web pages efficiently. Here are several best practices for increasing page speed and performance. Make sure your website is mobile-friendly and offers a consistent user experience across all devices:
Image compression: Use compressed image formats such as JPEG and PNG to reduce image file sizes without sacrificing quality. Image compression aids in the reduction of page loading times.
Enable browser caching: Use browser caching to store specific pieces of your website on visitors’ devices, eliminating the need to download them again and again. This can drastically reduce loading times for repeat visitors.
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Minification is the process of deleting extraneous characters from code files, such as spaces and comments, in order to reduce file size and improve page load times.
Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute static assets from your website across numerous servers in different geographic areas. This allows users from many regions to gain access to these content more quickly.
How to bootstrapping in your business https://startupadvice.in/bootstrapping-success-thrive-with-limited-resources/
Ensuring Proper Indexing
To ensure that your web pages get properly indexed by Google, follow these best practices:
XML Sitemaps: Create an XML sitemap that includes all of your website’s major pages. Submit the sitemap to Google Search Console to assist Google in quickly discovering and indexing your sites.
Robots.txt Best Practices: Use the robots.txt file to manage which pages or sections of your website should be crawled and indexed. Be cautious not to block critical pages or resources inadvertently.
Canonical URLs: Use canonical URLs to specify the preferred version of a web page when multiple versions of the same content exist (e.g., different URLs for mobile and desktop versions). This helps consolidate ranking signals and prevents duplicate content issues.
Avoiding Duplicate Content: Avoid having duplicate content on your website because search engines may not index all versions of the same content. To consolidate duplicate material under a single URL, use canonical tags and 301 redirects where appropriate.
Managing Pagination: For websites with paginated content, use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags to signal the relationship between paginated pages. This helps search engines understand the structure and index the content properly.
Handling JavaScript and AJAX: Make sure that crucial material isn’t hidden behind JavaScript or AJAX interactions, as Googlebot might not be able to render it efficiently. To ensure that material is accessible, use progressive enhancement approaches.
Common Indexing Issues and Solutions
Despite following best practices, indexing issues can still occur. Here are some common indexing issues and their solutions:
Blocked Resources: If certain resources (for example, CSS and JavaScript) are restricted in the robots.txt file, Googlebot will be unable to render the page appropriately. Check and update your robots.txt file to ensure that critical resources are accessible for crawling and indexing.
Noindex Tags and Directives: Double-check the code of your website for any noindex tags or directives that may prohibit specific pages from being indexed. To ensure that vital pages are indexed and ranked, remove these tags from them.
Mobile Indexing and Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP): Make sure your website is mobile-friendly and optimized for mobile-first indexing. Implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) can help increase mobile indexing and page load time for mobile consumers.
Server Errors and Connectivity Issues: Googlebot’s ability to crawl and index your website may be hampered by frequent server problems or connectivity issues. Keep an eye on your website’s server logs and address any recurrent problems as soon as possible.
Low-Quality Content and Thin Pages: If your website has low-quality or thin content, Google may choose not to index or rank those pages. Improve the content quality and give value to the pages to increase their chances of being indexed.
Monitoring Indexing Performance
To monitor your website’s indexing performance, use tools like Google Search Console and log file analysis. These tools provide valuable insights into crawling and indexing behavior, indexing errors, and the overall health of your website:
Google Search Console: Google Search Console offers reports on indexing coverage, crawl errors, and sitemap status. Monitor these reports regularly to identify any issues affecting your website’s indexing.
Crawling and Indexing Reports: Use log file analysis tools to review the crawl and indexing patterns of search engine bots. This study can assist in identifying areas for development and ensuring that all key pages are crawled and indexed.
Log File Analysis: Analyzing server log files provides detailed information about when and how search engine bots view your website. This information might help you understand how effectively your website gets crawled and indexed.
Conclusion: Indexing is a fundamental aspect of SEO that determines whether your web pages will be visible to users on search engines like Google. Understanding how Google indexes web pages and adhering to recommended practices for effective indexing are critical for increasing the visibility and organic traffic to your website. By optimizing your website’s architecture, content, and performance, as well as monitoring indexing performance, you can ensure that your web pages are crawled, indexed, and ranked in search engine results, allowing you to meet your SEO objectives while also offering meaningful content to your target audience.

Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.